Modular Construction

An Introduction to Process and Inspection
02 February 2021
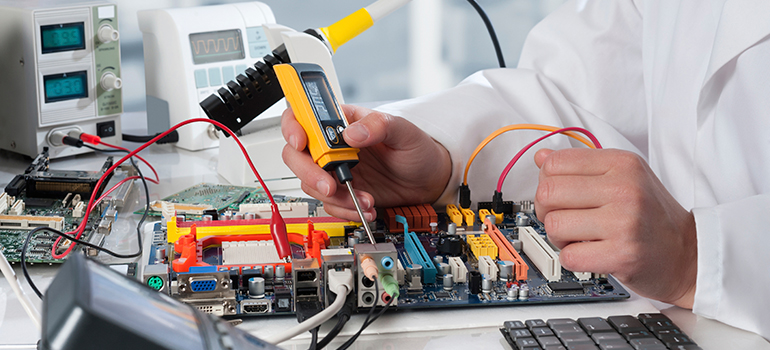
Modular construction is a process where building is constructed in a factory under controlled conditions, produced in modules that are then put together on site. They are built to the same codes as a site-built structure, using the same materials and methods, as well as standard operating procedures and inspection control points. They can be commercial or residential, and are assembled on permanent foundations as they are intended to be permanent structures once they are completed. Modular buildings are not to be confused with manufactured buildings, which have a permanent chassis to assure initial and continued transport.
Recently, there has been increasing demand from investors and developers to use modular construction, given the quality and savings it provides. With modern technology, almost any design is possible. For example, numerous hotels are currently being constructed in this manner, due to the effectiveness of getting the same quality over-and-over delivered to multiple locations. Additionally, faster building speeds, innovative design, eco-friendly innovations, and superior quality have led homeowners to turn to modular construction for housing needs.
Modular construction offers many benefits, including reduced time for completion, eliminating weather delays, reducing waste, fewer site disturbances, safer conditions, strong structures, and quality control and inspections during all phases of construction. These include controls and inspections implemented by the manufacturer to ensure materials and work meet the requirements of approved construction documents and referenced standards. Monitoring and inspection tasks are performed by an agency or firm other than the manufacturer.
As previously stated, modular construction is built to the same building codes as site-built structures throughout the nation. In the United States, each state regulates the modular industry differently. Many states have specific modular rules and regulations in place requiring the modular manufacturer to be contracted with an approved modular third-party inspection agency (TPIA). Very few states do not address modular construction; however, in these limited cases, it is left to the authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) to enforce the local and state building codes and requirements.
Inspections are conducted in the manufacturing facility by a certified, licensed inspectors at various hold points and phases of construction. Inspectors will need to witness any required testing as outlined in the quality assurance manual and all observations are documented in inspection reports. Once the building is found to be compliant with building codes, a label and state insignia are issued to assure the AHJ that the building has been reviewed and inspected by an approved TPIA.
In Canada, modular buildings must be certified to Canadian standards issued by the Standards Council of Canada (SCC), which requires evaluations of the factory quality systems and submitted design documents. An in-factory initial evaluation verifies quality and technical requirements with follow-up audits at frequency established by the certification body. Labels and specification sheets are then issued.
During assessments, a variety of conditions and characteristics are evaluated, including acoustics, energy, sustainability, the building envelope/enclosure, fire protection and air barrier. Additionally all applicable codes are considered and consulted, as is performance mockup and field testing. Inspections apply not only to the building but its components.
To ensure quality and performance and good time to market, it is extremely important that manufacturers, quality control and the third-party agencies work closely to verify all life safety elements of the building code are addressed. This will help ensure a successful build. Learn more about modular construction, industry trends, evaluation, and certification in our free webinar recording.

Ryan Knowles,
Project Manager
Ryan Knowles is the Manager of the Industrial Building Program at Intertek. He has more than 20 years in the modular industry in the manufacturing and regulatory aspects of the modular industry and holds 21 International Code Council certificates in numerous construction trades, as well as various state credentials specific to the modular industry.

Peter Gildenstern,
Manager - Manufactured Housing and Calibration Services
Peter Gildenstern is the Manager of Certification Services for Manufactured Structures at Intertek Testing Services in Coquitlam, British Columbia. With more than 30 years' experience in the design and code compliance of various building components and factory-built structures, he manages the accredited calibration lab involved in certifying various types of structural testing equipment.